Human Robot Interactions
Vitality Forms can be leveraged to enhance the relationship between humans and robots by improving the actions a robot can perform through the integration of an affective component. While this trait is inherently human, it can also be implemented in robotics.
An example from one of the last studies
Our studies have demonstrated that kinematic modulation occurs when a robot performs actions, whether gentle or rude, in the presence of a human observer.
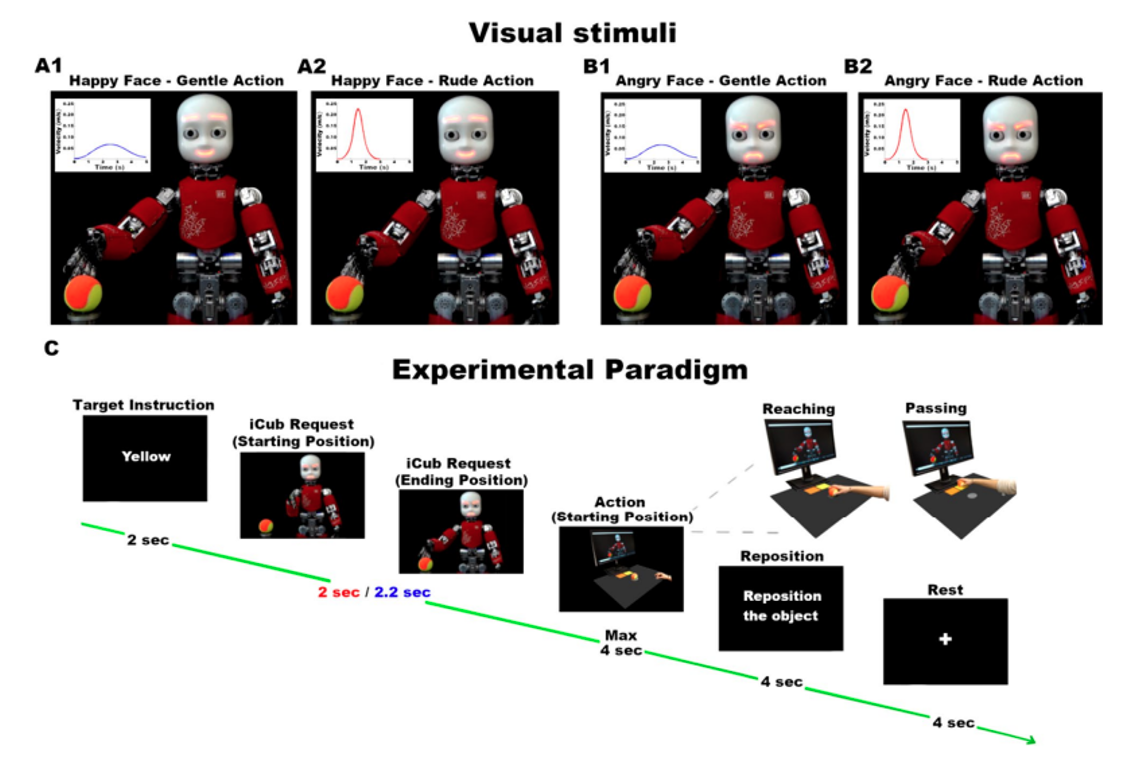
Visual stimuli representing the iCub robot giving request performed gently (blue curves, A1–B1) or rudely (red curves, A2–B2) with a happy (A1–A2) or an angry (B1–B2) facial expression. Experimental paradigm (C). Participants received an instruction regarding the color (Target Instruction, 2 s), observed the iCub robot request (gentle: 2.2 s, rude: 2 s) and performed the action (reaching and passing, max 4 s). Finally, they were asked to place the ball in the starting position with their lef hand (Reposition, 4 s) and to wait the new trial while observing a white fxation cross on a black screen (Rest, 4 s). (Vannucci et al., 2024
If you want to read more about this topic, click here Article PDF
References
Vannucci, F., Lombardi, G., Rea, F., Sandini, G., Di Cesare, G., & Sciutti, A. (2024). Humanoid Attitudes Influence Humans in Video and Live Interactions. IEEE Access, 2024, DOI 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3442863