Techniques
Real Time Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Our research team is currently implementing real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (real-time fMRI) on a GE 3 Tesla scanner. Real-time fMRI is an advanced neuroimaging technique that enables simultaneous measurement and observation of brain activity while people perform tasks. This approach allows us to noninvasively modulate brain activity in specific brain regions, providing a unique opportunity to examine its causal influence on behavior.
Kinematics
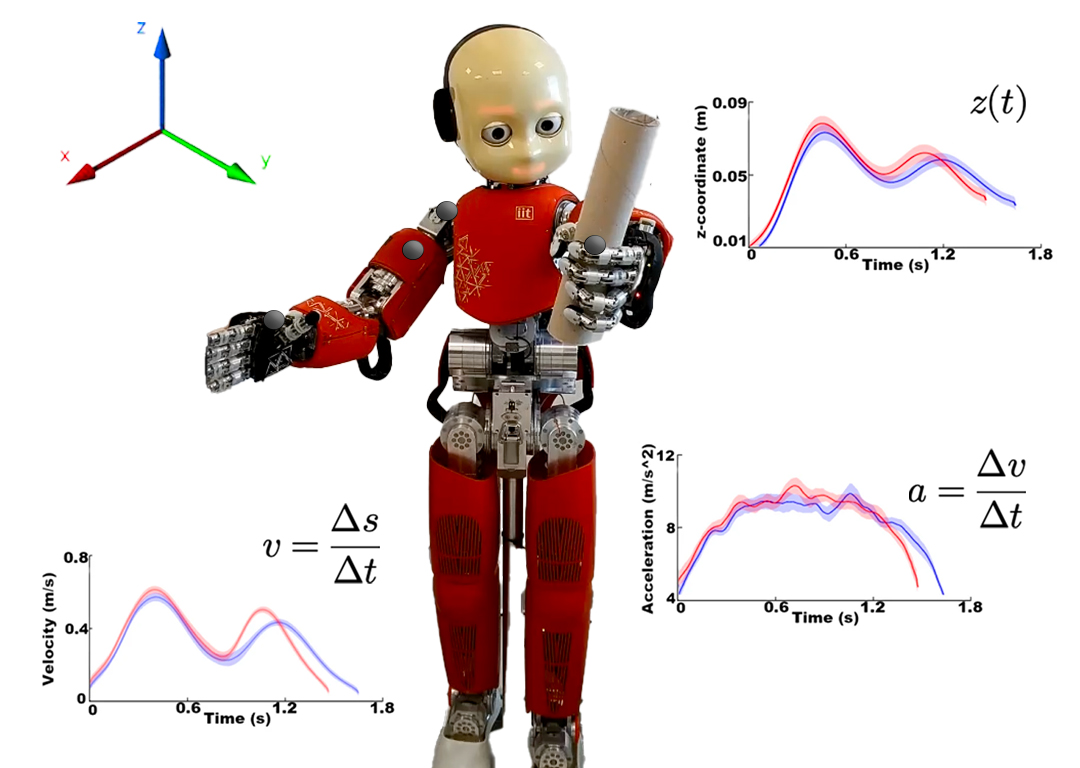
Most of our previous studies have investigated the kinematic features of actions conveying different VFs within non-naturalistic experimental settings (with visual or auditory stimuli). Moving forward, we aim to investigate these kinematic signatures in more ecologically valid contexts, focusing on real human–human and human–robot interactions. We record these action features using motion capture systems (Optitrack V120 Trio, Vicon, and MR_cam). These systems track body movements by detecting passive markers placed on specific anatomical landmarks (for example the right hand).
Physiological Measurements
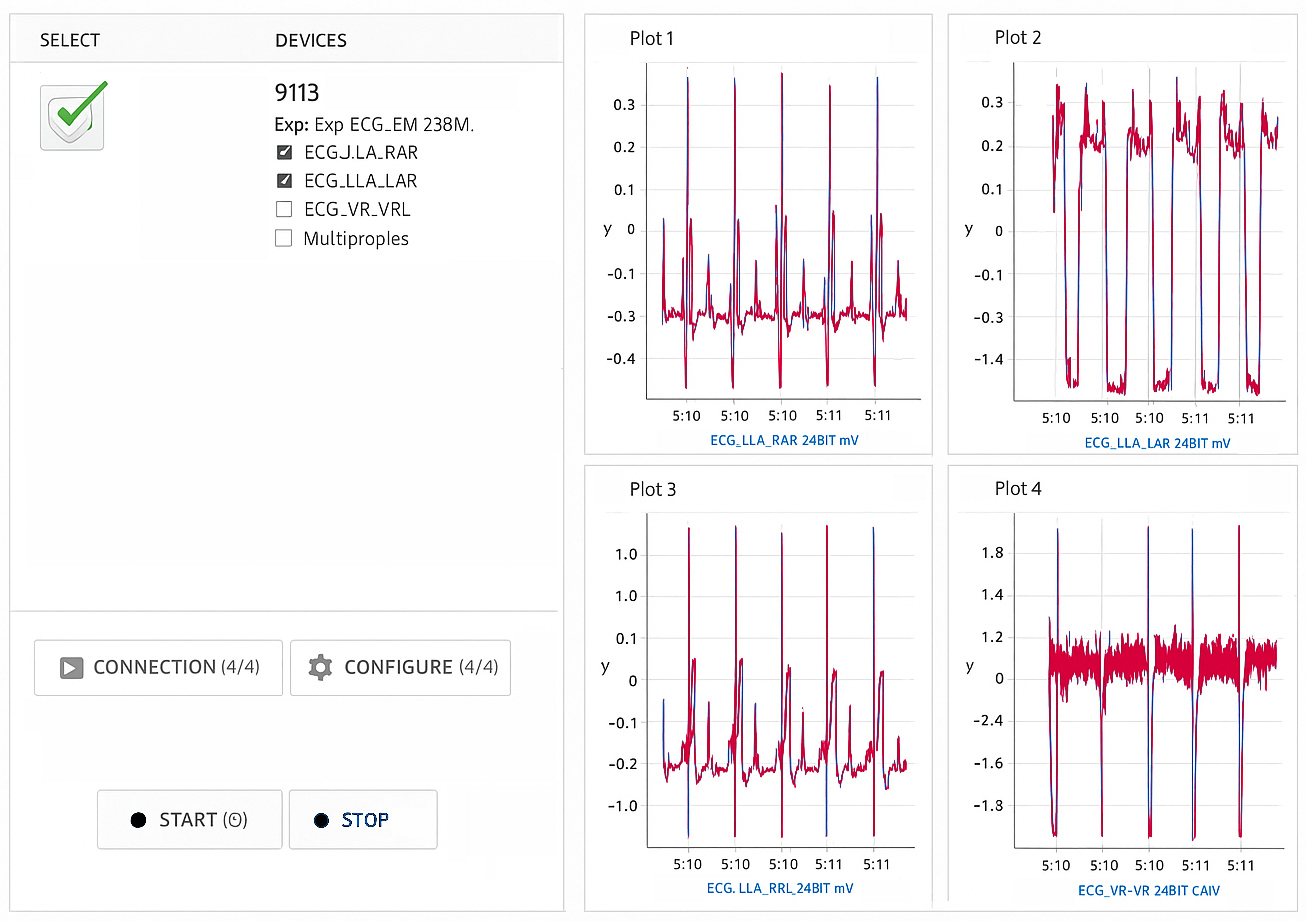
We employ a variety of methodologies and instruments to measure and analyze physiological variables that characterize social interactions. Currently, our techniques include electrocardiogram (ECG) to monitor the heart’s electrical activity, the electromyography (EMG) to assess the electrical activity of muscles and eye-tracking to monitor and analyze eye movements, providing insights into visual attention, cognitive processes, and affective states.
Psychophysics
To study the mechanisms underlying the perception of VFs we use psychophysics parameters such as estimation times and reaction times. For example, it has been shown that vocal requests conveying different forms of vitality can influence the perception of goal-directed actions by affecting the estimation of action duration.